West Germanic languages
Group of languages / From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Dear Wikiwand AI, let's keep it short by simply answering these key questions:
Can you list the top facts and stats about West Germanic language?
Summarize this article for a 10 years old
The West Germanic languages constitute the largest of the three branches of the Germanic family of languages (the others being the North Germanic and the extinct East Germanic languages). The West Germanic branch is classically subdivided into three branches: Ingvaeonic, which includes English and Frisian, Istvaeonic, which encompasses Dutch and its close relatives, and Irminonic, which includes German and its close relatives and variants.
| West Germanic | |
|---|---|
| Geographic distribution | Originally between the Rhine, Alps, Elbe, and North Sea; today worldwide |
| Linguistic classification | Indo-European
|
| Subdivisions | |
| ISO 639-5 | gmw |
| Linguasphere | 52-AB & 52-AC |
| Glottolog | west2793 |
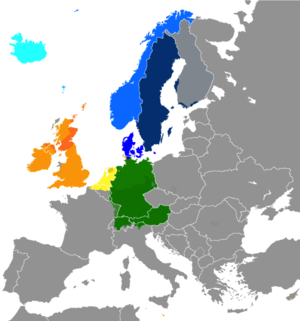 Extent of Germanic languages in present day Europe North Germanic languages West Germanic languages Dots indicate areas where multilingualism is common. | |
English is by far the most-spoken West Germanic language, with more than 1 billion speakers worldwide. Within Europe, the three most prevalent West Germanic languages are English, German, and Dutch. Frisian, spoken by about 450,000 people, constitutes a fourth distinct variety of West Germanic. The language family also includes Afrikaans, Yiddish, Low Saxon, Luxembourgish, and Scots. Additionally, several creoles, patois, and pidgins are based on Dutch, English, or German.