Tibetan Plateau
Plateau in Central, South and East Asia / From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Dear Wikiwand AI, let's keep it short by simply answering these key questions:
Can you list the top facts and stats about Tibetan Plateau?
Summarize this article for a 10 years old
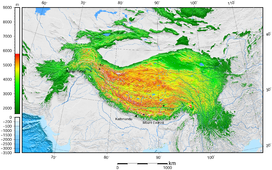
The Tibetan Plateau (Tibetan: བོད་ས་མཐོ།, Wylie: bod sa mtho), also known as the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau[1] or the Qing–Zang Plateau[2] (Chinese: 青藏高原; pinyin: Qīng–Zàng Gāoyuán) or as the Himalayan Plateau in India,[3][4] is a vast elevated plateau located at the intersection of Central, South and East Asia[5][6][7][8][9][10][11][12] covering most of the Tibet Autonomous Region, most of Qinghai, western half of Sichuan, Southern Gansu provinces in Western China, southern Xinjiang, Bhutan, the Indian regions of Ladakh and Lahaul and Spiti (Himachal Pradesh) as well as Gilgit-Baltistan in Pakistan, northwestern Nepal, eastern Tajikistan and southern Kyrgyzstan. It stretches approximately 1,000 kilometres (620 mi) north to south and 2,500 kilometres (1,600 mi) east to west. It is the world's highest and largest plateau above sea level, with an area of 2,500,000 square kilometres (970,000 sq mi) (about five times the size of Metropolitan France).[13] With an average elevation exceeding 4,500 metres (14,800 ft)[citation needed] and being surrounded by imposing mountain ranges that harbor the world's two highest summits, Mount Everest and K2, the Tibetan Plateau is often referred to as "the Roof of the World".
| Tibetan Plateau | |
|---|---|
| 青藏高原 (Qīng–Zàng Gāoyuán, Qinghai–Tibet Plateau) | |
 The Tibetan Plateau lies between the Himalayan range to the south and the Taklamakan Desert to the north. (Composite image) | |
| Dimensions | |
| Length | 2,500 km (1,600 mi) |
| Width | 1,000 km (620 mi) |
| Area | 2,500,000 km2 (970,000 sq mi) |
| Geography | |
| Location | |
| Range coordinates | 33°N 88°E |
 | |
The Tibetan Plateau contains the headwaters of the drainage basins of most of the streams and rivers in surrounding regions. This includes the three longest rivers in Asia (the Yellow, Yangtze, and Mekong). Its tens of thousands of glaciers and other geographical and ecological features serve as a "water tower" storing water and maintaining flow. It is sometimes termed the Third Pole because its ice fields contain the largest reserve of fresh water outside the polar regions. The impact of climate change on the Tibetan Plateau is of ongoing scientific interest.[14][15][16][17]