
Guadeloupe
Overseas department of France in the Caribbean / From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Dear Wikiwand AI, let's keep it short by simply answering these key questions:
Can you list the top facts and stats about Guadeloupe?
Summarize this article for a 10 years old
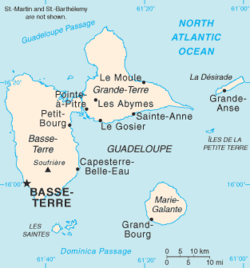
Guadeloupe (/ˌɡwɑːdəˈluːp/; French: [ɡwad(ə)lup] ⓘ; Guadeloupean Creole French: Gwadloup, IPA: [ɡwadlup]) is an archipelago and overseas department and region of France in the Caribbean.[4] It consists of six inhabited islands—Basse-Terre, Grande-Terre, Marie-Galante, La Désirade, and the two inhabited Îles des Saintes—as well as many uninhabited islands and outcroppings.[5] It is south of Antigua and Barbuda and Montserrat and north of the Commonwealth of Dominica. The region's capital city is Basse-Terre, located on the southern west coast of Basse-Terre Island; however, the most populous city is Les Abymes and the main centre of business is neighbouring Pointe-à-Pitre, both located on Grande-Terre Island.[4] It had a population of 384,239 in 2019.[6]
Guadeloupe
| |
|---|---|
| Anthem: La Marseillaise ("The Marseillaise") | |
 | |
 | |
| Country | |
| Prefecture | Basse-Terre |
| Departments | 1 |
| Government | |
| • President of the Departmental Council | Guy Losbar[1] |
| • President of the Regional Council | Ary Chalus |
| Area | |
| • Total | 1,628 km2 (629 sq mi) |
| • Rank | 16th region |
| Highest elevation | 1,467 m (4,813 ft) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 383,559 |
| • Density | 240/km2 (610/sq mi) |
| Demonym | Guadeloupean |
| Time zone | UTC-4:00 (AST) |
| ISO 3166 code | |
| GDP (2014)[3] | Ranked 15th region in France |
| Total | €8.1 billion (US$10.3 bn) |
| Per capita | €19,810 (US$25,479) |
| Largest metropolitan area | Pointe-à-Pitre |
| Currency | Euro (€) (EUR) |
| Website | www www |
Like the other overseas departments, it is an integral part of France. As a constituent territory of the European Union and the Eurozone, the euro is its official currency and any European Union citizen is free to settle and work there indefinitely. However, as an overseas department, it is not part of the Schengen Area. The region formerly included Saint Barthélemy and Saint Martin, which were detached from Guadeloupe in 2007 following a 2003 referendum.
Christopher Columbus visited Guadeloupe in 1493, during his second voyage, and gave the island its name. The official language is French; Antillean Creole is also spoken.[4][5]
