German language
West Germanic language / From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Dear Wikiwand AI, let's keep it short by simply answering these key questions:
Can you list the top facts and stats about German language?
Summarize this article for a 10 years old
German (Standard High German: Deutsch, pronounced [dɔʏtʃ] ⓘ) is a West Germanic language mainly spoken in Western Europe and Central Europe. It is the most widely spoken and official or co-official language in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, Liechtenstein, and the Italian province of South Tyrol. It is also an official language of Luxembourg and Belgium, as well as a recognized national language in Namibia. Outside Germany, it is also spoken by German communities in France (Alsace), Czech Republic (North Bohemia), Poland (Upper Silesia), Slovakia (Košice Region, Spiš, and Hauerland), and Hungary (Sopron).
| German | |
|---|---|
| Native to | Germany, Austria, Switzerland, Luxembourg, Belgium and Liechtenstein |
| Region | German-speaking Europe |
| Ethnicity | Germans (Austrians, Swiss, Luxembourgers) |
Native speakers | 95 million (2014)[1] L2 speakers: 80–85 million (2014)[1] |
Standard forms | |
| |
| Signed German | |
| Official status | |
Official language in | |
Recognised minority language in | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | de |
| ISO 639-2 | ger (B) deu (T) |
| ISO 639-3 | Variously:deu – Germangmh – Middle High Germangoh – Old High Germangct – Colonia Tovar Germanbar – Bavariancim – Cimbriangeh – Hutterite Germanksh – Kölschnds – Low German[note 1]sli – Lower Silesianltz – Luxembourgish[note 2]vmf – Mainfränkischmhn – Mòchenopfl – Palatinate Germanpdc – Pennsylvania Dutchpdt – Plautdietsch[note 3]swg – Swabian Germangsw – Swiss Germanuln – Unserdeutschsxu – Upper Saxonwae – Walser Germanwep – Westphalianhrx – Riograndenser Hunsrückischyec – Yenish |
| Glottolog | high1289 High Germanfran1268 Middle Germanhigh1286 Upper German |
| Linguasphere | 52-ACB–dl (Standard German) |
 | |
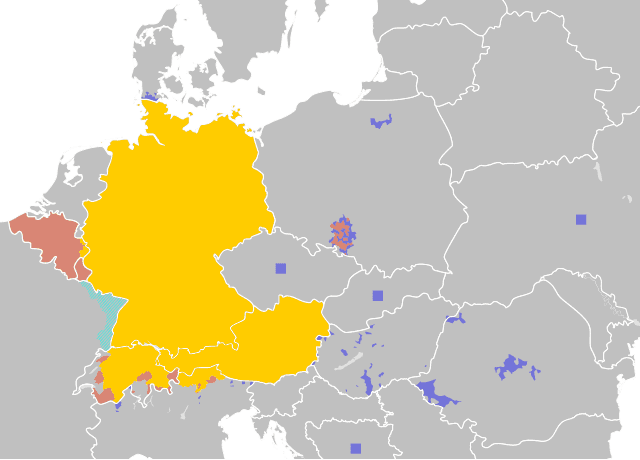
 (Co)official majority language
Co-official minority language
Statutory minority/cultural language
Non-statutory minority language | |
| This article contains IPA phonetic symbols. Without proper rendering support, you may see question marks, boxes, or other symbols instead of Unicode characters. For an introductory guide on IPA symbols, see Help:IPA. | |
German is most similar to other languages within the West Germanic language branch, including Afrikaans, Dutch, English, the Frisian languages, Low German, Luxembourgish, Scots, and Yiddish. It also contains close similarities in vocabulary to some languages in the North Germanic group, such as Danish, Norwegian, and Swedish. German is the second-most widely spoken Germanic language after English, which is also a West Germanic language.
German is one of the major languages of the world. It is the most spoken native language within the European Union. German is also widely taught as a foreign language, especially in continental Europe, where it is the third most taught foreign language (after English and French), and the United States. The language has been influential in the fields of philosophy, theology, science, and technology. It is the second-most commonly used scientific language and among the most widely used languages on websites. The German-speaking countries are ranked fifth in terms of annual publication of new books, with one-tenth of all books (including e-books) in the world being published in German.
German is an inflected language, with four cases for nouns, pronouns, and adjectives (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative); three genders (masculine, feminine, neuter); and two numbers (singular, plural). It has strong and weak verbs. The majority of its vocabulary derives from the ancient Germanic branch of the Indo-European language family, while a smaller share is partly derived from Latin and Greek, along with fewer words borrowed from French and Modern English.
German is a pluricentric language; the three standardized variants are German, Austrian, and Swiss Standard German. Standard German is sometimes referred as High German while referring to its regional origin of the High German languages. It is also notable for its broad spectrum of dialects, with many varieties existing in Europe and other parts of the world. Some of these non-standard varieties have become recognized and protected by regional or national governments.
Since 2004, heads of state of the German-speaking countries have met every year[8] and the Council for German Orthography has been the main international body regulating German orthography.